- Products
- Resources
-
-
Vicks products are available for purchase online and in-store at most major retailers.
-
-
- Support
-
-
VICKS SUPPORT
View product-specific FAQs & videos
-
-
- Products
- Resources
- SUPPORT
- Warranty Registration
- Contact Us
What are the different types of orthopedic implants?
orthopedic implants play a crucial role in modern medicine. They assist in repairing bones, joints, and ligaments. Dr. Sarah Thompson, a renowned orthopedic surgeon, states: "Orthopedic implants are essential for restoring function and improving patients' quality of life."
There are various types of orthopedic implants, each designed for specific conditions. These include intramedullary nails, plates, screws, and joint replacements. Each implant type has unique features that cater to different injuries and patient needs. Understanding these implants can guide treatment decisions.
However, not all orthopedic implants perform perfectly. Some patients may experience complications like infection or implant failure. Continuous research and innovation aim to enhance implant design and biocompatibility. This pursuit raises questions about the longevity and effectiveness of materials used in orthopedic implants. Challenges remain on the path to developing the perfect solution for every patient.
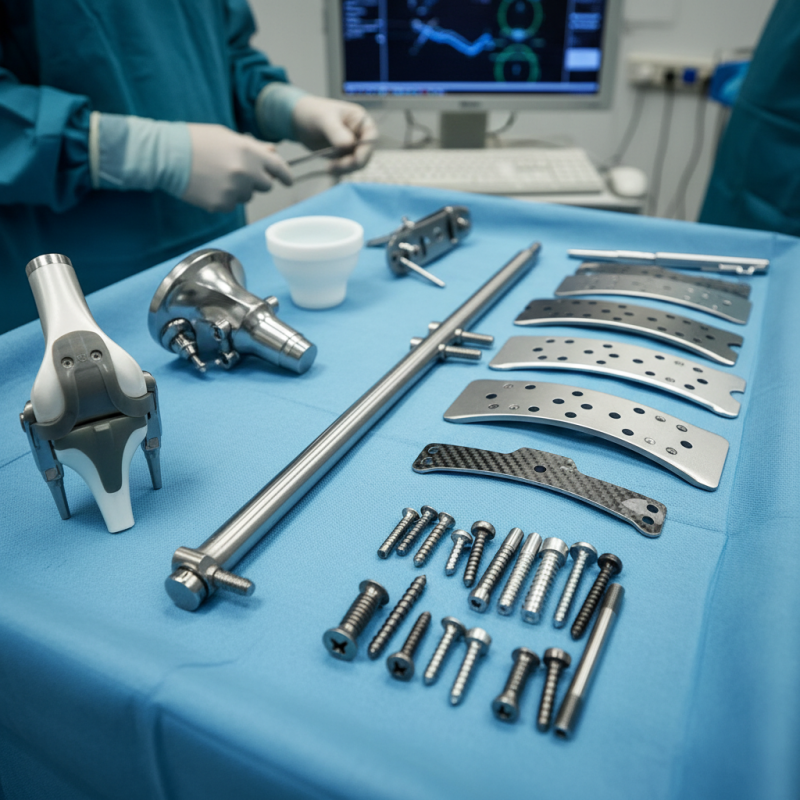
Types of Orthopedic Implants Based on Material Composition
Orthopedic implants can be categorized based on their material composition. Many implants are made from metals like titanium and stainless steel. Titanium is popular due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It also resists corrosion well. This makes it ideal for long-term use in the body. Stainless steel is another common choice. It's durable and cost-effective, but it may not be as biocompatible as titanium.
Ceramic implants are becoming increasingly popular. They offer great wear resistance and are often used in joint replacements. However, they can be brittle and more likely to break under stress. Another material, biodegradable polymers, is emerging. These can gradually dissolve in the body, which may reduce the need for a second surgery. Yet, their long-term reliability is still under scrutiny.
Each material has its pros and cons. Choosing the right one is crucial. Some surgeons may prefer metals for their proven track record. Others might see the potential of ceramics or biodegradable options. Balancing functionality, comfort, and safety is a challenge. It involves understanding the specific needs of each patient. Ongoing research could help refine these materials further. As technologies improve, the future of orthopedic implants looks promising.
Types of Orthopedic Implants Based on Material Composition
| Implant Type | Material Composition | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Screws | Titanium, Stainless Steel | Fracture fixation |
| Plates | Stainless Steel, Cobalt Chrome | Bone stabilization |
| Nails | Titanium, Stainless Steel | Intramedullary fixation |
| Joint Prostheses | Cobalt Chrome, Polyethylene | Joint replacement |
| Bone Grafts | Demineralized Bone Matrix, Calcium Phosphate | Bone regeneration |
Classification of Orthopedic Implants by their Functionality
Orthopedic implants are classified based on their functionality. This classification helps surgeons choose the right type for each patient's needs. Load-bearing implants, for instance, support weight and stress during movement. They are crucial in the healing process of broken bones. Common types include plates and screws, which stabilize fractures effectively.
Non-load-bearing implants serve different purposes. They are often used for fixation or as scaffolds for tissue growth. These implants, such as pins and rods, help guide healing without bearing weight. They can be temporary solutions. Choosing the right implant type is essential for success. Miscommunication about functionality can lead to complications, prolonging recovery.
Some implants are biodegradable. These materials dissolve in the body over time, reducing the need for a second surgery. However, their effectiveness and longevity can vary. The trade-offs may lead to questions. Is the healing process adequate? Will there be risks associated with dissolution? Each case is unique and requires thorough evaluation.
Common Types of Joint Replacement Implants Used in Orthopedics
Joint replacement surgery is a common procedure in orthopedics. It often involves the use of various implants designed to restore function and relieve pain. These implants can be made from metal, plastic, or ceramic materials. Common joint replacements include hip, knee, and shoulder implants. Each type has its unique design and purpose.
Hip implants usually consist of a stem, a ball, and a cup. The stem fits into the thigh bone. The ball replaces the hip joint’s head. The cup sits in the pelvis, providing stability.
Knee implants often come in several pieces. They are designed to mimic the natural movement of the joint. These implants help reduce pain and improve mobility.
Shoulder replacements can be more complex. Some designs are total replacements, while others are partial, depending on the damage.
Despite advancements, not all implants work perfectly for everyone. Some patients experience discomfort or limited movement after surgery. It’s crucial to have realistic expectations. Regular check-ups can help identify any issues with the implants early on. This proactive approach can ensure better long-term outcomes for patients.
Overview of Bone Fixation Devices and Their Applications
Orthopedic implants are crucial in bone fixation. These devices help stabilize fractures and promote healing. Common types include plates, screws, and rods. Each type serves a specific purpose based on the injury location and severity.
Bone plates are flat devices attached to the bone with screws. They provide stability and support during recovery. Screws are used alone or with plates. They help hold bone fragments together securely. Rods are often utilized in long bone fractures. They are inserted into the marrow canal to maintain alignment.
Tips: Always discuss options with a healthcare professional. Understand the risks and benefits of each device. It's essential to follow post-operative care instructions closely. Healing can be a slow process, requiring patience. Healing isn’t always linear; setbacks can happen, and that’s okay. Adjust expectations as needed, and don't hesitate to seek guidance.
Emerging Technologies in Orthopedic Implant Design and Development
Emerging technologies are reshaping orthopedic implant design and development. Innovations like 3D printing are changing how implants are created. This method allows for customization, fitting each patient perfectly. Surgical procedures can now focus on precision, which was not possible before.
Materials are also evolving. Biocompatible materials are being tested to reduce rejection rates. These materials promote faster healing and integration with bone. Smart implants with sensors are on the horizon. They could monitor the healing process and send data to healthcare providers. Imagine an implant that can alert doctors about complications.
Despite these advancements, challenges remain. Research is still needed to ensure long-term effectiveness. The integration of smart technology poses risks of failure or malfunction. Not every new technology translates seamlessly from concept to surgery. Continuous reflection and adjustment are crucial in this evolving field. Each step forward in orthopedic implants sparks new questions and potential hurdles.